This article starts with the most basic and most commonly used electronic components and basic circuits, and introduces some problems that should be paid attention to during circuit design to improve the reliability and anti-interference ability of the designed circuit.
First, the basic components
1, resistance
1) Basic concepts
We all know that the formula I = U/R also knows that P = UI. A resistor is a non-energy storage component that directly converts electrical energy into heat. Therefore, if the power consumed by the resistor is too large, it will overheat it. And burned.
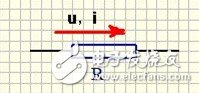
2) Basic parameters
Resistance, accuracy, power. We should pay attention to the following issues when using:
In digital circuits, most of the resistance requirements of resistors are not very high (such as the use of pull-up and pull-down resistors), so the type of resistance should be reduced as much as possible to facilitate procurement and production.
Only in the case of high precision requirements, such as feedback resistors for power supplies and op amps, we use high-precision resistors (typically 1%). In most cases, we use 5% precision resistors.
In a circuit that flows a relatively large current, we should calculate the power consumed by the resistor. Otherwise, if the actual power consumed is greater than its rated power, the resistor will be burned out.
2, the capacitor
1) Basic concepts
We should know a few basic formulas:
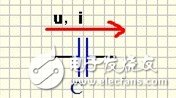
2) Characteristic parameters
Capacitance, accuracy, withstand voltage, leakage current, frequency characteristics. When using it, we should pay attention to the following issues:
Withstand voltage: If the voltage applied to the capacitor is higher than the rated voltage that it can withstand, it will cause the capacitor to breakdown and burn. Therefore, no matter how much higher than the actual working voltage, the capacitor withstand voltage is higher than this. Optional, otherwise the voltage will be burned out if the voltage exceeds the withstand voltage.
Leakage current: Leakage current refers to the current between the metal parts with electrical insulation in the electrical insulation, or between the live parts and the grounded parts in the absence of a fault applied voltage. The current formed by the surrounding medium or the insulating surface is called leakage. Current. The polarity capacitor is further divided into a forward leakage current and a reverse leakage current. The reverse leakage current is large. When a reverse voltage is connected across the polarity capacitor, the reverse leakage current is large, P=U· I, the capacitor will be burned, which is why the polarity capacitance must not be reversed.
Frequency characteristics: In the actual circuit, the capacitor is equivalent to the capacitor and the resistor in parallel and then connected in series with the inductor. It is inductive at high frequencies and capacitive at low frequencies. High-frequency filtering uses a monolithic capacitor with a small capacitance, and an electrolytic capacitor with a large capacitance when low-frequency filtering.
3, inductance
1) Basic concepts
Inductance is a property of a closed loop. When the coil passes current, a magnetic field induction is formed in the coil, which in turn generates an induced current to resist current flow through the coil. The interaction between this current and the coil is called the electrical inductive reactance, which is the inductance. The unit is "Henry (H)".
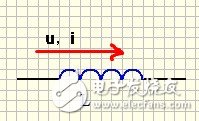
2) Characteristic parameters
Including inductance, accuracy, saturation current, operating frequency, operating current inductance, as shown in the figure, the inductor is composed of a ferrite core and a copper wire wound around it. When there is no core, the inductance is small.
Working current: In the actual circuit, the inductance is equivalent to a resistor connected in series. When the current passes, it will generate eddy current to form heat. The inductance is too small, and the current passing through is large. W=1/2·L·i2 will cause overheating and burning. inductance.
4, diode
1) Basic concepts
A diode is also called a crystal diode, or a diode. It is an electronic device with unidirectional conduction current.
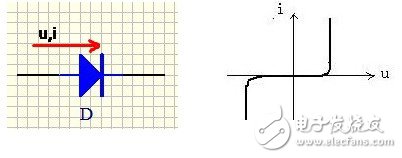
2) Characteristic parameters
Including working current, forward conduction voltage, reverse voltage, forward conduction time, reverse recovery time
Positive conduction voltage: When the forward voltage is applied, the forward voltage is small at the beginning of the forward characteristic, which is insufficient to overcome the blocking effect of the electric field in the PN junction. The forward current is almost zero. This segment is called the dead zone. . This forward voltage that does not turn the diode on is called the deadband voltage. When the forward voltage is greater than the deadband voltage, the electric field in the PN junction is overcome, the diode is forward-conducting, and the current rises rapidly as the voltage increases. In the current range of normal use, the terminal voltage of the diode remains almost constant during turn-on. This voltage is called the forward voltage of the diode.
Reverse voltage: When the applied reverse voltage does not exceed a certain range, the current through the diode is the reverse current formed by the minority carrier drift motion. Since the reverse current is small, the diode is in an off state. If the reverse voltage is too large, the diode will be broken down.
Positive conduction time and reverse recovery time: In the actual digital circuit, the forward and reverse recovery of the diode takes a certain amount of time to complete. In order to improve the stability of the circuit system, we should shorten the conduction and recovery as much as possible. Time, Schottky diodes are commonly used, commonly known as fast diodes.
5, triode
1) Basic concepts
Semiconductor triodes are also known as "transistors" or "transistors." It is a semiconductor electronic device that can function as amplification, oscillation or switching.

2) Characteristic parameters
Including power consumption, frequency characteristics
Frequency characteristics: The triode has three working intervals, a cut-off area, an amplification area and a saturation area. The amplified state is also called the linear operating state, Ic = ß · Ib, used in analog circuits. The cutoff and saturation states, also known as switch states, are used in digital circuits.
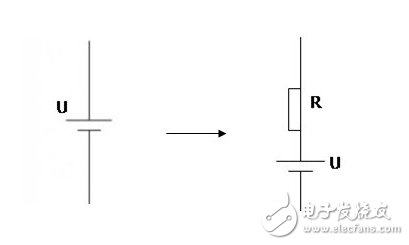
6, power
In the actual circuit, the power supply has an internal resistance, which is equivalent to a series resistor. At this time, the output voltage will decrease, and the interference in the circuit can not be ignored.
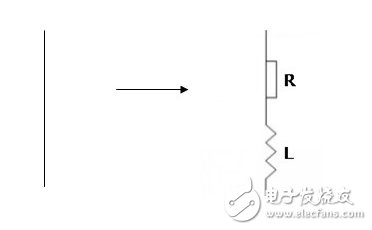
7, wire
In the actual circuit, the wire has a certain internal resistance, R=Ï·L/S, which is quite in series with the inductor and the resistor. Since the inductor itself has a eddy current effect, the designer should design the wire in the circuit, especially in the high-frequency circuit. Try to be as short as possible and as thick as possible.
Electric Burner
Electric Burner,Electrical Spiral Burner,Double Hotplate Burner,Single Hotplate Burner
Shaoxing Haoda Electrical Appliance Co.,Ltd , https://www.zjhaoda.com