Zinc oxide arrester features _ zinc oxide arrester working principle _ zinc oxide arrester model meaning
**1. Introduction to Zinc Oxide Arrester**
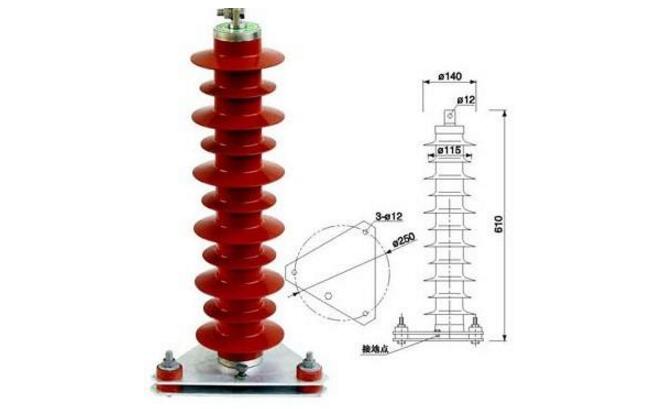
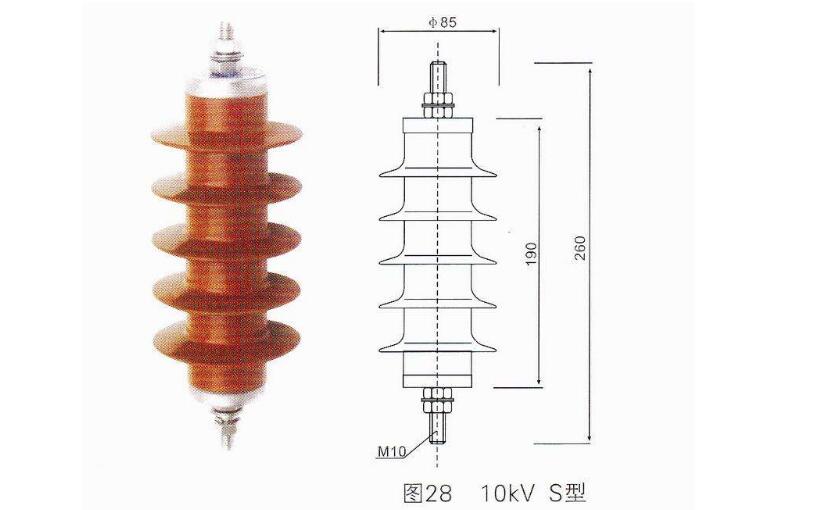
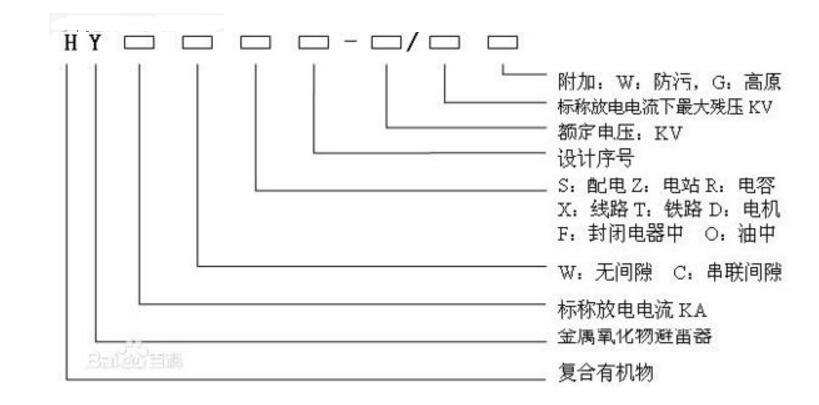
Zinc oxide arresters are advanced protective devices developed in the 1970s, designed to safeguard electrical equipment from overvoltage events such as lightning strikes and switching surges. These arresters primarily consist of zinc oxide varistors, which exhibit non-linear voltage-current characteristics. Under normal operating conditions, when the voltage is below the varistor's threshold, the device behaves like an insulator with high resistance. However, during overvoltage situations—such as lightning strikes—the varistor rapidly conducts, allowing large currents to flow to ground and limiting the voltage to a safe level. Once the overvoltage subsides, the varistor returns to its high-resistance state, ensuring the system continues to operate normally. This makes zinc oxide arresters highly effective in protecting power systems and connected equipment from damage caused by transient voltages.

Cold shrinkable cable accessories are made of elastomer materials (commonly used silicone rubber and ethylene-propylene rubber) injected and vulcanised in the factory, and then expanded and lined with plastic spiral supports to form various components of cable accessories. Field installation, these pre-expanded parts in the treated cable ends or joints, pull out the internal support of the plastic spiral strip (support), pressed on the cable insulation and the composition of the cable accessories. Because it is at room temperature by elastic retraction force, rather than like heat shrinkable cable accessories to be heated by fire shrinkage, so commonly known as cold shrinkable cable accessories. Early cold shrink cable termination head just additional insulation using silicone rubber cold shrink parts, electric field processing is still using stress cone type or stress band wrapping type.
Universal use of cold shrinkage stress control tube, voltage level from 10kv to 35kv. cold shrink cable joints, 1kv level using cold shrink insulation tube as reinforced insulation, 10kv level with internal and external semi-conductive shielding layer of the joints cold shrink insulation parts. Three-core cable terminal bifurcation using cold shrink branch sleeve.
Cold Shrink Tube,Cold Shrinkable tubing,Cold-shrink tube,Cold shrinkage pipe,shrink tube,Cold Shrink Cable Accessories
Mianyang Dongyao New Material Co. , https://www.mydyxc.com