Mitsubishi PLC Index Register Usage:
Radiators, essential yes, but sometimes they`re pretty ugly. I can say this from personal experience, as a discoloured radiator sits in my hallway bringing down the decor. Faced with the option of replacing it at great cost, I`m now thinking a splash of paint might be the better option.
That theory is backed up by seeing this bold painted radiator transformation!
Painted Radiator,Finned Painted Radiator,Distribution Finned Painted Radiator,Painted Transformer Cooling Radiator Shenyang Tiantong Electricity Co., Ltd. , https://www.ttradiator.com
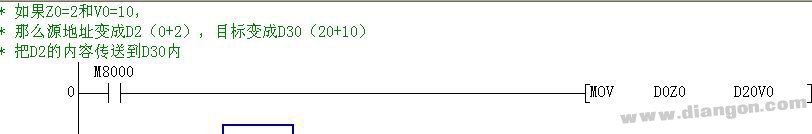
Image:

Image:

Image:
The Mitsubishi PLC index register is a key component used in programming and data manipulation. It comes in two main types: V (16-bit word element) and Z (also 16-bit word element). These registers can be read from and written to just like regular data registers, making them versatile for various operations.
When working with 32-bit operations, the V and Z registers are often used together, with Z representing the lower 16 bits and V the higher 16 bits. This combination allows for more complex data handling and improved program efficiency.
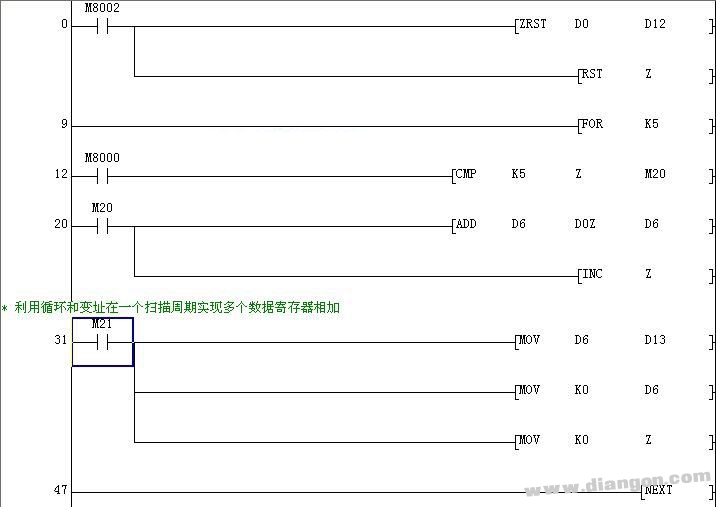
In the FX2N series, there are 8 pairs of index registers: V0–V7 and Z0–Z7. These registers are commonly used to modify address numbers or perform indexed addressing in function instructions. They allow for flexible referencing of devices, which simplifies the structure of complex programs and makes them easier to maintain and debug.
Index registers are especially useful when you need to access multiple data points dynamically. For example, they can be used to point to different memory locations based on a variable value, which is essential in applications such as data logging, control loops, and sequence processing.
Understanding how to use index registers effectively can significantly improve your ability to write efficient and scalable PLC programs.